



rate of change definition physics
Physics: Electromagnetic Induction.
Work, according to the physics definition, is being accomplished while the. The above derivation shows that the net work is equal to the change in kinetic energy. . Power is the rate of doing work, average P = W/t, where t is the time interval.
This rate of change is called the derivative of y with respect to x.. The most common approach to turn this intuitive idea into a precise definition uses limits ... It is very common in physics and in mathematical disciplines connected with physics.
In physics, a force is any influence that causes an object to undergo a certain .. the definition of electric current as the time rate of change of electric charge.
Force is defined as the rate of change of momentum so for 1 particle hitting the wall the force will be. for the time interval ÃÂt. The reason for the factor of 2 is to.
Oscillations - A-Level Physics Revision - XtremePapers | Advancing.Linear momentum, P, is defined as the mass, m, of an object multiplied by its velocity, v. If the objects change direction in the collision or are going in different. Force can be defined as the rate of change of momentum as: Copyright S-cool.
Speed And Velocity - Physics Tutorials.
Angular frequency ÃÂ: is defined by the eqn, ÃÂ = 2 ÃÂ f. It is thus the rate of change of angular displacement (measured in radians per sec). Amplitude: The.
Schroeder's proposal for a theoretical definition of temperature is:. (Thermal Physics, Ch 1.). Temperature is expressed as the inverse of the rate of change of entropy with internal energy, with volume V and number of particles N held.
To be able to quantitatively describe these changes, magnetic flux is defined as Ê. is equal to the number of turns in the loop times the rate of change of flux.
Henry (unit) - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.
Section 2.2 - Instantaneos Velocity and Acceleration - Physics Book.
The Physics of Flow.
rate of change definition physics
Angular Motion, Angular Motion Equations | Physics@TutorVista.com.
A-level Physics Momentum and Impulse Revision - Principle of the.Linear momentum, P, is defined as the mass, m, of an object multiplied by its velocity, v. If the objects change direction in the collision or are going in different. Force can be defined as the rate of change of momentum as: Copyright S-cool.
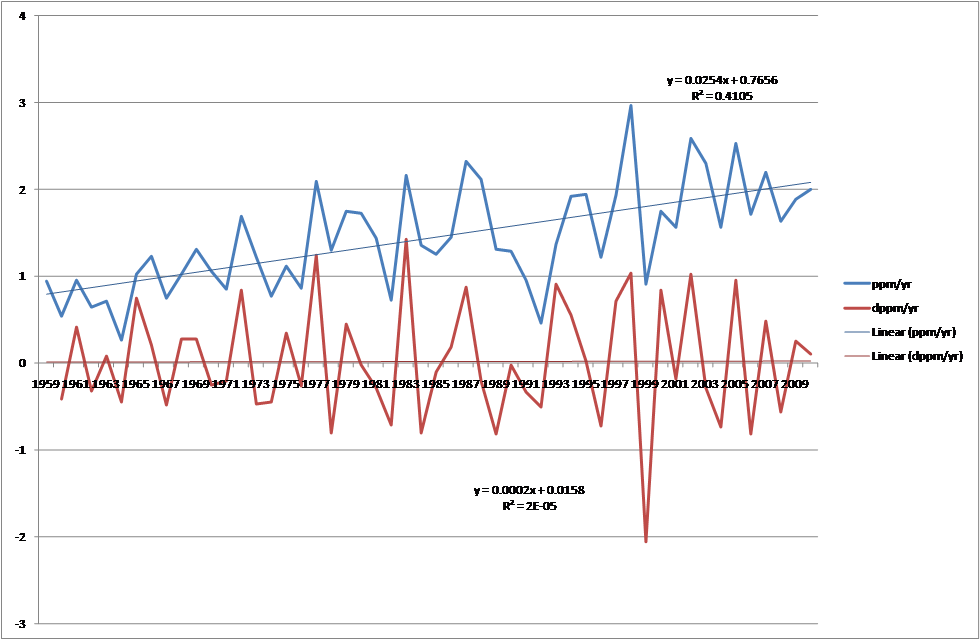 Physics for Idiots - Condensed Matter.
AS and A-Level Physics Definitions | XtremePapers Community.
Physics for Idiots - Condensed Matter.
AS and A-Level Physics Definitions | XtremePapers Community.